Category: Javascript
JavaScript中获取元素的绝对位置
在一些应用中,可能会有需要知道某一个控件在页面中的位置,在网上比较容易找到下面这个解决方法。
在页面中有一个按钮:
|
1 2 |
<input id="a" type="button" value="click me to get position" onclick="getPos(this)" /> |
在脚本中响应点击事件的是这个函数:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
function getPos(e){ var t=e.offsetTop; var l=e.offsetLeft; while(e=e.offsetParent){ t+=e.offsetTop; l+=e.offsetLeft; } alert("top="+t+"\nleft="+l); } |
这个方法的实现相当精炼,意思就是先取得自己的相对位置,再叠加其最近的相对位置容器(offsetParent,它不一定是其父节点)的相对位置,直至顶层位置容器(一般就是body),从而得出该节点的相对位置。
不过,很快就发现这个函数也许并不够用,因为我在页面里有可能使用了一些CSS来使得本来平铺的画面变成一个滚动区域,例如设置了父节点的height为 某个值,并且其overflow设为auto或者scroll。这时,上面的方法因为没有计算其滚动偏移,所以所得的值不一定是元素当前的绝对位置,所以 我对上面的方法进行了一些小改动,实际上就是加入了对其滚动偏移量的计算。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
function getPosition(sender) { var e=sender,E=e; var x=e.offsetLeft; var y=e.offsetTop; while (e=e.offsetParent) { var P=e.parentNode; while (P!=(E=E.parentNode)) { x-=E.scrollLeft; y-=E.scrollTop; } x+=e.offsetLeft; y+=e.offsetTop; E=e; } return {"x":x,"y":y}; //alert("top="+y+"\nleft="+x); } |
稍微测试了一下,基本上在IE和FF中都能正常运转。
在运用方面,由于使用到往上遍历,如果节点树结构过于复杂,而且有不会有滚动出现的话,那么还是用第一个方法就足够了。
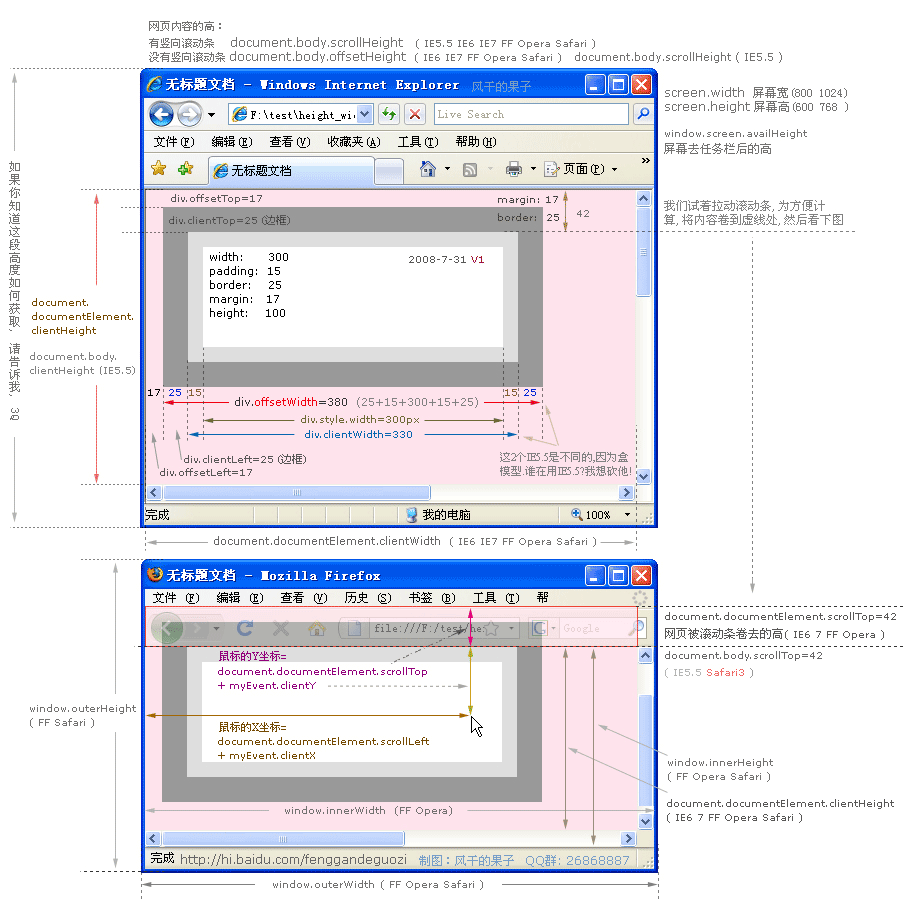
scrollLeft,scrollWidth,clientWidth,offsetWidth之完全详解
scrollHeight: 获取对象的滚动高度。
scrollLeft:设置或获取位于对象左边界和窗口中目前可见内容的最左端之间的距离
scrollTop:设置或获取位于对象最顶端和窗口中可见内容的最顶端之间的距离
scrollWidth:获取对象的滚动宽度
offsetHeight:获取对象相对于版面或由父坐标 offsetParent 属性指定的父坐标的高度
offsetLeft:获取对象相对于版面或由 offsetParent 属性指定的父坐标的计算左侧位置
offsetTop:获取对象相对于版面或由 offsetTop 属性指定的父坐标的计算顶端位置
event.clientX 相对文档的水平座标
event.clientY 相对文档的垂直座标
event.offsetX 相对容器的水平坐标
event.offsetY 相对容器的垂直坐标
document.documentElement.scrollTop 垂直方向滚动的值
event.clientX+document.documentElement.scrollTop 相对文档的水平座标+垂直方向滚动的量
以上主要指IE之中,FireFox差异如下:
IE6.0、FF1.06+:
clientWidth = width + padding
clientHeight = height + padding
offsetWidth = width + padding + border
offsetHeight = height + padding + border
IE5.0/5.5:
clientWidth = width - border
clientHeight = height - border
offsetWidth = width
offsetHeight = height
(需要提一下:CSS中的margin属性,与clientWidth、offsetWidth、clientHeight、offsetHeight均无关)

非常齐全的document body window div 高度、宽度、鼠标坐标图解
分享几个js牛人的blog
JQuery的作者:http://ejohn.org/
Pro Javascript Techniques里面提到的:
http://dean.edwards.name/
http://dean.edwards.name/weblog/
以后有新的再补充~~
Javascript学习笔记–类的继承
最近在看天雪发给我看的一本Javascript的书,是JQuery之父写的,写得很棒,里面推荐的资源也很棒。为了弥补我的差记性,特写下学习笔记。
http://javascript.crockford.com/inheritance.html
这个是讲Js里面的类继承的写法,这个作者太犯贱了,上面的例子都是用自己写的方法,结果方法在最下面才写出来,告诉我们。搞得我一开始以为是内置的方法呢。。。不过他的方法写得太酷了,下面列举一下:
Sugar(作者管他写的方法叫做糖,确实很甜)
To make the examples above work, I wrote four sugar methods. First, the method method, which adds an instance method to a class.
为了上面的例子跑起来,我写了四个很甜的方法。首先,是method方法,它是用来把方法添加到class里的。
|
1 2 3 4 |
Function.prototype.method = function (name, func) { this.prototype[name] = func; return this; }; |
This adds a public method to the Function.prototype, so all functions get it by Class Augmentation. It takes a name and a function, and adds them to a function's prototype object.
It returns this. When I write a method that doesn't need to return a value, I usually have it return this. It allows for a cascade-style of programming.
Next comes the inherits method, which indicates that one class inherits from another. It should be called after both classes are defined, but before the inheriting class's methods are added.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
Function.method('inherits', function (parent) { var d = {}, p = (this.prototype = new parent()); this.method('uber', function uber(name) { if (!(name in d)) { d[name] = 0; } var f, r, t = d[name], v = parent.prototype; if (t) { while (t) { v = v.constructor.prototype; t -= 1; } f = v[name]; } else { f = p[name]; if (f == this[name]) { f = v[name]; } } d[name] += 1; r = f.apply(this, Array.prototype.slice.apply(arguments, [1])); d[name] -= 1; return r; }); return this; }); |
Again, we augment Function. We make an instance of the parent class and use it as the new prototype. We also correct the constructor field, and we add the uber method to the prototype as well.
The uber method looks for the named method in its own prototype. This is the function to invoke in the case of Parasitic Inheritance or Object Augmentation. If we are doing Classical Inheritance, then we need to find the function in the parent's prototype. The return statement uses the function's apply method to invoke the function, explicitly setting this and passing an array of parameters. The parameters (if any) are obtained from the arguments array. Unfortunately, the arguments array is not a true array, so we have to use apply again to invoke the array slice method.
Finally, the swiss method.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Function.method('swiss', function (parent) { for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i += 1) { var name = arguments[i]; this.prototype[name] = parent.prototype[name]; } return this; }); |
The swiss method loops through the arguments. For each name, it copies a member from the parent's prototype to the new class's prototype.
才翻译了一个,发现懒得翻译了。。。实在是个懒人啊。。。大家将就着看,我什么时候想到了再来翻译一下好了,其实都是很简单的英语。